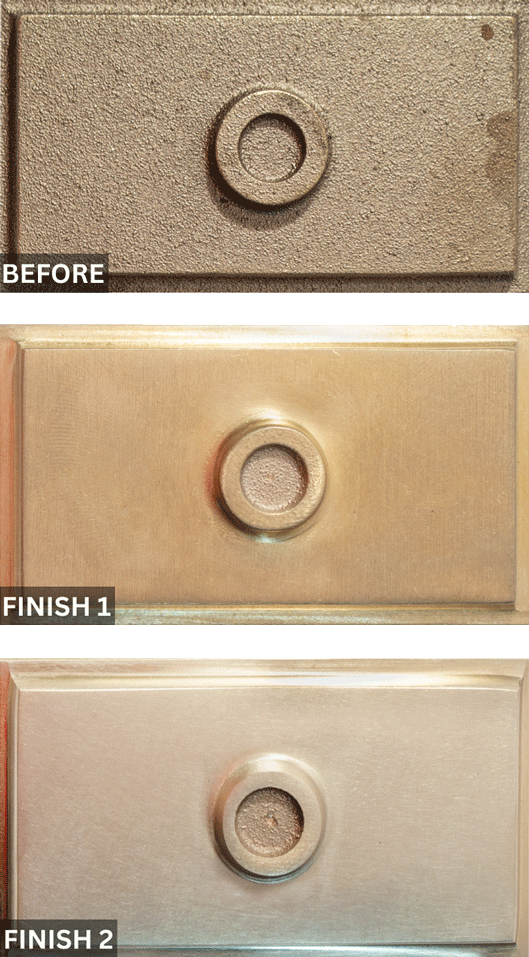
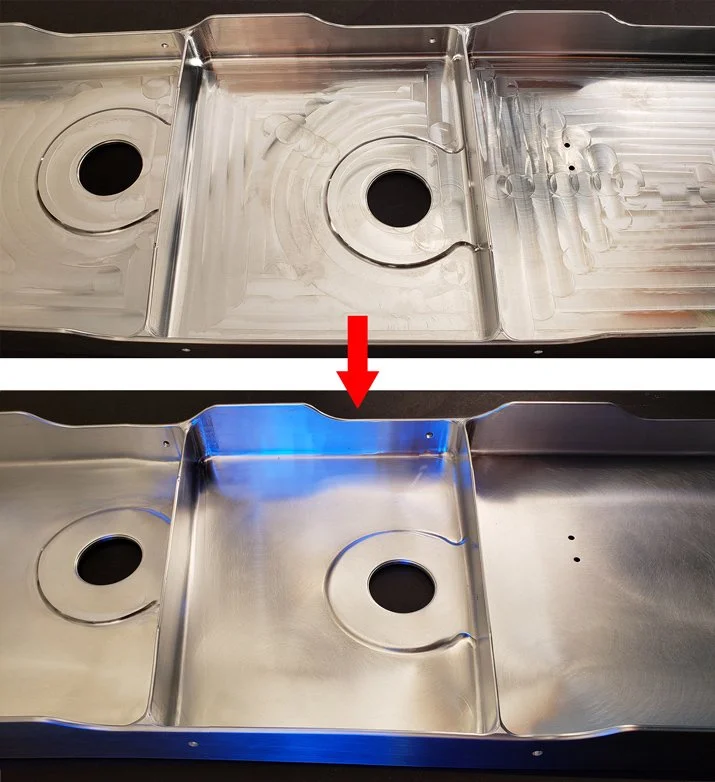
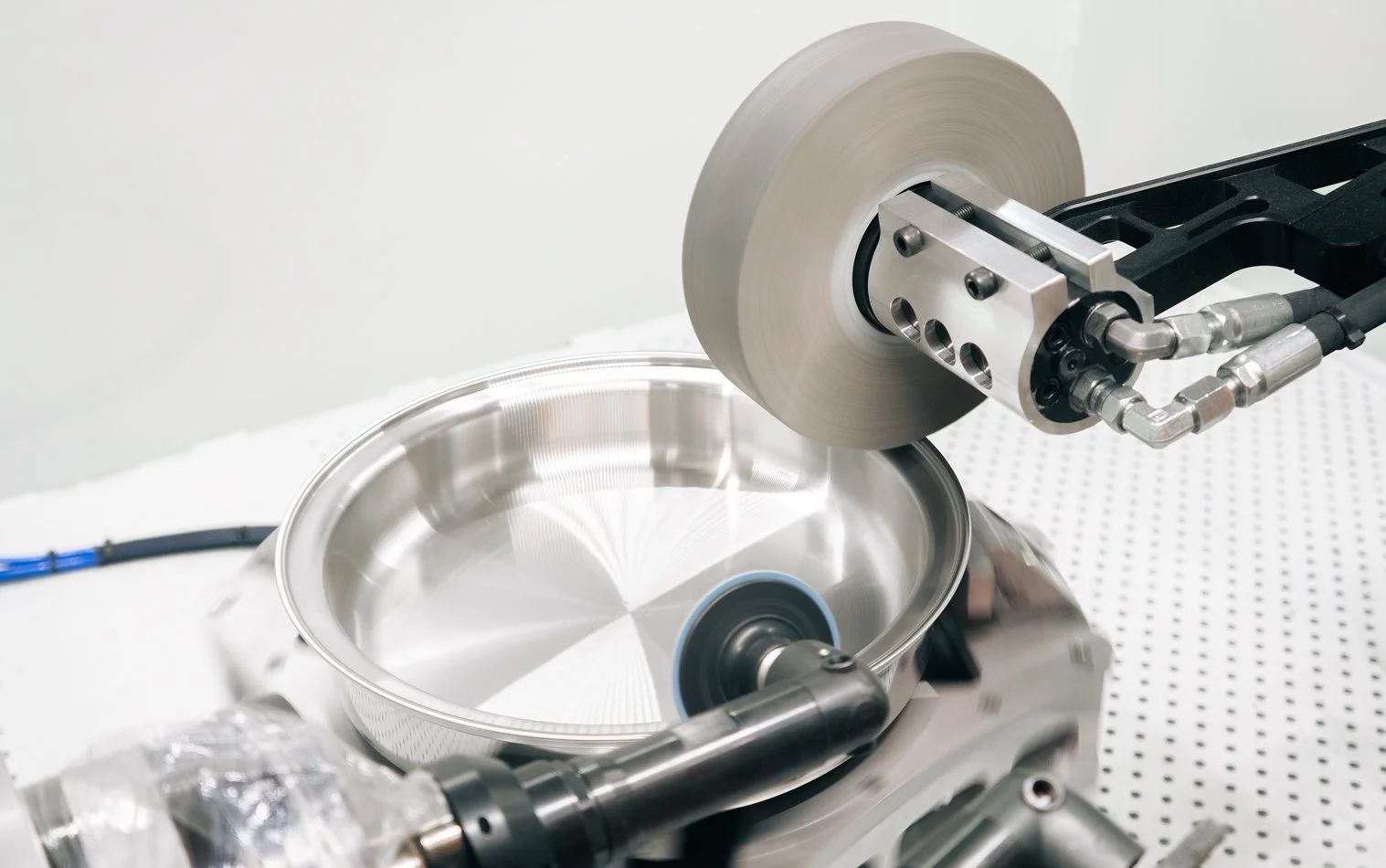
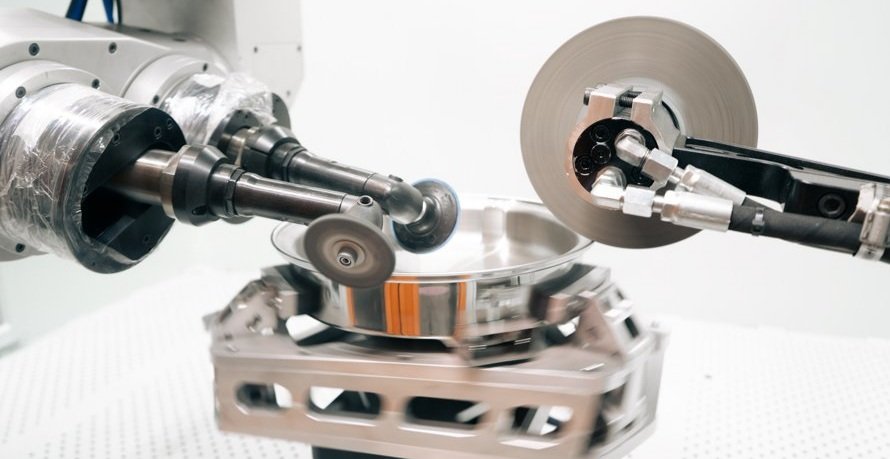
What Is Gear Shaping?
In precision manufacturing, producing accurate and reliable gears requires the right cutting process and just as importantly, proper finishing. The gear shaping process is one of the most versatile gear-cutting methods used today, especially for complex and internal gear geometries.
Understanding Gear Shaping and Deburring in Manufacturing
In precision manufacturing, producing accurate and reliable gears requires the right cutting process and just as importantly, proper finishing. The gear shaping process is one of the most versatile gear-cutting methods used today, especially for complex and internal gear geometries. This article explores what gear shaping is, how it differs from other gear-cutting methods, and why deburring and finishing are critical steps after shaping.
What Is Gear Shaping?
Gear shaping is a machining process used to cut gear teeth using a reciprocating cutting tool, known as a gear shaper cutter. The cutter and the workpiece rotate in a synchronized motion while the cutter moves up and down, gradually forming the gear teeth to the required profile.
Unlike continuous cutting processes, gear shaping removes material in incremental strokes. This makes it especially well suited for producing internal gears, splines, and gears with complex or interrupted geometries that cannot be easily produced through other methods.
Gear shaping is widely used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, defense, and heavy equipment manufacturing, where precision and flexibility are essential.
How Does Gear Shaping Differ From Other Gear Cutting Methods?
Gear shaping is one of several methods used to create gear teeth. Each process has strengths depending on the gear design and production requirements.
Gear Shaping:
Uses a reciprocating cutter and excels at producing internal gears and gears located close to shoulders or obstructions. It offers high accuracy and flexibility but is generally slower than continuous cutting processes.
Gear Hobbing:
Uses a rotating hob in a continuous cutting motion. It is highly efficient for producing external spur and helical gears in high volumes but cannot produce internal gears.
Gear Milling:
Uses a form cutter on a milling machine. It is often used for prototypes, repairs, or low-volume production runs but lacks the speed and precision of shaping or hobbing.
Gear Broaching:
Removes the full gear profile in a single pass using a broach. It is extremely fast for high-volume production but requires specialized tooling and is less flexible.
Gear shaping remains a preferred solution when gear geometry or part constraints limit the use of other cutting methods.
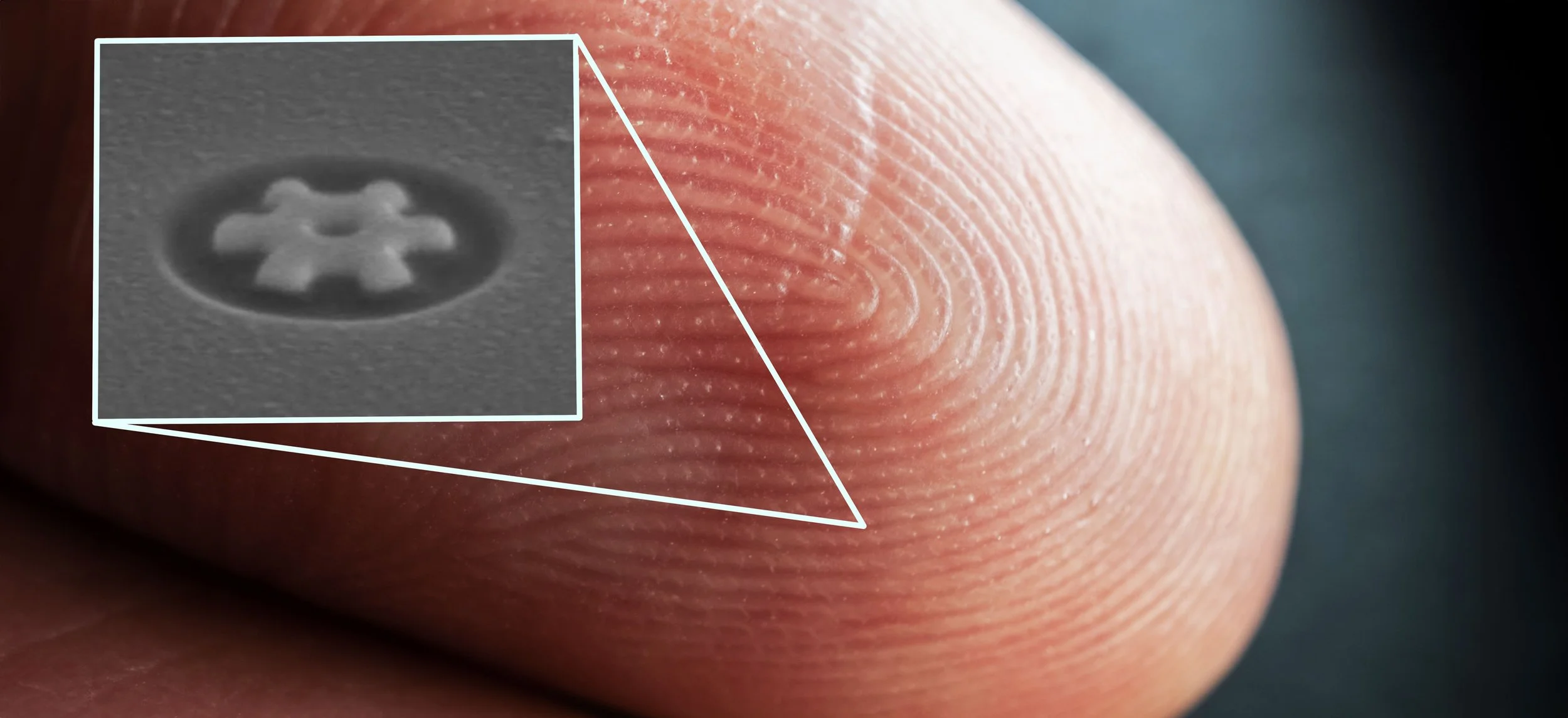
Why Is It Important to Remove Burrs After Gear Shaping?
Like all gear-cutting processes, gear shaping produces burrs small, sharp edges or raised material left behind at the tooth edges and root of the gear. These burrs are a natural byproduct of metal removal but can create serious issues if left unaddressed.
Burrs can:
Create safety hazards during handling and assembly
Interfere with proper gear meshing and performance
Accelerate wear and noise in gear systems
Prevent accurate inspection and measurement
In high-precision applications, even minimal burrs can negatively affect performance and reliability.
Why Is Deburring Necessary for Shaped Gears?
Deburring is the process of removing burrs and refining sharp edges after machining. For shaped gears, deburring is not simply a cosmetic step it is essential to overall gear function and longevity.
Proper deburring:
Improves gear engagement and load distribution
Reduces stress concentrations at tooth edges
Enhances surface finish and dimensional accuracy
Ensures gears meet quality and safety standards
As gear designs become more complex and tolerances tighter, consistent and repeatable deburring becomes increasingly important.
What Is the Effect of Proper Gear Deburring?
The effects of effective deburring extend well beyond appearance:
Improved Durability:
Removing burrs reduces the risk of micro-cracks and premature gear failure.
Enhanced Precision:
Clean edges allow gears to perform as designed, especially in high-load or high-speed applications.
Better Surface Finish:
A smoother finish improves efficiency, reduces friction, and can help prevent corrosion.
Increased Manufacturing Efficiency:
Well-finished gears assemble more easily, operate more reliably, and reduce costly rework or downtime.
Gear Shaping and Finishing With James Engineering
While gear shaping produces accurate and complex gear geometries, the process is not complete without proper finishing. That’s where James Engineering plays a critical role in the manufacturing workflow.
James Engineering specializes in automated deburring and edge-finishing solutions designed to handle the demands of precision-machined components, including shaped gears. Their machines are built to deliver consistent, repeatable results whether the application requires lights-out automation for high-volume production or flexible setups for complex parts.
By integrating advanced deburring and finishing systems after gear shaping, manufacturers can ensure their gears meet performance, safety, and quality requirements without sacrificing efficiency.
Conclusion
Gear shaping is a powerful and versatile gear-cutting process, particularly for internal and complex gear designs. However, the true performance of a shaped gear depends on what happens after cutting. Deburring and finishing are essential steps that protect functionality, extend service life, and uphold manufacturing quality.
Understanding gear shaping and pairing it with the right finishing solution helps manufacturers produce gears that perform reliably in even the most demanding applications.
Automatic Deburring and Chamfering
Metal finishing is no longer a secondary operation, it’s a defining factor in product quality, production efficiency, and long-term manufacturing success.
Automated Metal Finishing That Scales: The James Engineering Advantage
Metal finishing is no longer a secondary operation, it’s a defining factor in product quality, production efficiency, and long-term manufacturing success. As parts become more complex and production demands increase, manufacturers are under pressure to deliver consistent finishes at higher volumes with fewer resources. This is where James Engineering stands apart.
James Engineering designs and builds advanced automated metal finishing machines that replace slow, inconsistent manual processes with precision-driven, repeatable results. From deburring and chamfering to polishing, radiusing, and surface finishing, our MAX Systems redefine what modern finishing equipment should be.
The Problem with Traditional Metal Finishing
Many manufacturers still rely on outdated finishing methods: hand deburring, tumbling, fixed robotic cells, or single-purpose machines. While these approaches may work in limited scenarios, they often introduce bottlenecks, quality variation, and excessive labor costs, especially as part complexity and volume increase.
Manual finishing struggles with consistency. Tumbling lacks control. Robotic systems can be expensive, inflexible, and difficult to retool. In high-mix or high-volume environments, these limitations add up quickly.
James Engineering built MAX Systems specifically to solve these challenges.
One Platform. Unlimited Finishing Capability.
The MAX Machine is not a single-purpose tool, it’s a modular, multi-function finishing platform. Designed to accommodate an unlimited array of tool heads, MAX can deburr, chamfer, polish, radius, and surface-finish parts within the same system.
Quick-change tooling allows operators to transition between processes in minutes, not hours. This means fewer machines on the floor, less downtime between jobs, and a dramatic increase in overall throughput.
Whether you’re finishing small precision components or large industrial parts, MAX adapts to the job, not the other way around.
Precision Through Compliant Technology
At the core of every James Engineering machine is patented compliant technology. Unlike rigid systems that rely on fixed pressure and perfect part conditions, MAX dynamically adapts to part geometry, surface variation, and tool wear in real time.
The result is consistent material removal without over-grinding, edge burn, or part damage. Even complex geometries, internal features, and irregular contours are finished evenly and repeatably.
This level of control allows manufacturers to achieve high-end finishes while extending tool life and reducing scrap.
Built for High Volume, Ready for Lights-Out
Efficiency doesn’t stop at cycle time. James Engineering machines are engineered to eliminate setup delays, operator dependency, and unnecessary downtime.
Saved finishing “recipes” allow operators to recall exact cycles with a single button press. This enables fast changeovers, repeatable results, and seamless production across shifts or product lines.
For manufacturers pushing throughput even further, MAX Systems can be configured for fully automated, lights-out operation, running unattended while maintaining the same precision and consistency as attended cycles.
Full OEM Control Means Full Customization
James Engineering is a full OEM manufacturer. Every component, from machine frames and control arms are designed and built in-house.
This gives us complete control over performance, reliability, and customization. Machines can be tailored to specific materials, part sizes, cycle requirements, and future expansion needs. As production evolves, MAX Systems evolve with it.
This is not a one-size-fits-all solution, it’s a platform engineered around your operation.
Sustainable by Design
Modern manufacturing demands smarter use of resources. James Engineering machines support optional wet finishing cycles with closed-loop filtration systems that recycle fluids for reuse. Combined with long-life abrasives and compliant engagement that prevents overuse, MAX Systems significantly reduce consumable waste.
No scrap. Longer tool life. More efficient finishing. Sustainability is built into the process, not added as an afterthought.
Proven Across Industries, Built for What’s Next
James Engineering machines are trusted by manufacturers across aerospace, automotive, defense, medical, additive manufacturing, and heavy industry. From small precision parts to high-volume production runs, MAX Systems deliver consistent results at scale.
We’ve helped manufacturers increase output, reduce labor, improve quality, and future-proof their finishing operations, right in our hometown in Colorado and across coastlines.
Supporting the Next Stage of Your Manufacturing Operation
Every manufacturing operation evolves. The systems that worked yesterday were the right tools for their time and the companies that succeed long-term are the ones that know when it’s time to take the next step.
James Engineering exists to support that evolution. Our MAX Systems are designed for manufacturers who are growing, refining processes, and looking for ways to increase consistency, throughput, and flexibility without disrupting what already works. We don’t replace experience, we build on it.
By integrating advanced automation, compliant technology, and modular tooling, James Engineering helps manufacturers elevate their finishing operations while protecting quality, labor efficiency, and long-term investment. The result is not a dramatic overhaul, but a confident step forward.
From facilities in our hometown in Colorado to operations across coastlines, we work alongside manufacturers as a trusted partner, adapting machines to real production needs and supporting the people who keep those operations running.
If you’re exploring ways to strengthen your finishing process, streamline production, or prepare for future demand, James Engineering is here to support you. Contact our team to learn how a MAX System can complement your operation and help your customers continue to win.
What Does Our Machine Change Over Look Like?
Most setups would require a different machine — but not this one. In this video, we demonstrate the fast and seamless changeover on our MAX Systems Automatic Deburring System. Watch how we go from one metal part to a completely different one in minutes,
MAX Systems Deburring Changeover Demo
We just finished machining a gear… But what happens when the next part is completely different?
No center. No clamp point. Totally unique geometry.
Most setups would require a different machine — but not this one. In this video, we demonstrate the fast and seamless changeover on our MAX Systems Automatic Deburring System. Watch how we go from one metal part to a completely different one in minutes, with custom tooling and modular fixturing that adapts to almost any shape.
Mixed and Rare Metal Finishing
Mixed and Rare Metal Finishing: Deburr Techniques and Benefits
While many metals are straightforward to machine using standard equipment, mixed and rare earth metals possess unique chemical properties that necessitate specialized machining processes.
Understanding Mixed Metals and Why Finishing Mixed and Rare Metals Requires Specialized Techniques, Surface Finishing
Mixed and Rare Metal Finishing: Techniques and Benefits
Machine metal processing is a crucial part of manufacturing, where metal parts are transformed through alterations in shape, dimensions, properties, and finishes to create finished products. While many metals are straightforward to machine using standard equipment, mixed and rare earth metals possess unique chemical properties that necessitate specialized machining processes.
Understanding Mixed Metals
Mixed metals, also known as alloys, are combinations of two or more metals that result in enhanced properties. Here are some common mixed metals, their properties, and applications:
Brass: Known for its malleability and ease of cold and hot forming, brass is used in keys, connectors, radiators, and musical instruments.
Bronze: Appreciated for its corrosion resistance and strength, bronze is ideal for gears, pumps, diaphragms, and architectural fittings.
Copper: Renowned for its ductility and conductivity, copper is extensively used in electrical wiring, semiconductors, and antimicrobial surfaces.
The Role of Rare Earth Metals
Rare earth metals, a group of 17 elements, are not rare in abundance but are seldom found in economically viable concentrations. Their unique properties make them irreplaceable in certain applications, despite their processing challenges.
Notable Rare Metals and Their Uses
Magnesium: Lightweight and strong, magnesium is used in laptop enclosures, automotive transmissions, and small electronics.
Zirconium: With exceptional resistance to hydrochloric acid and ease of welding, zirconium finds use in nuclear reactors, pumps, and chemical processing equipment.
Titanium: Strong, corrosion-resistant, and biocompatible, titanium is essential in medical implants, aerospace components, and high-performance automotive parts.
Finishing Methods for Mixed and Rare Metal Parts
Finishing methods for rare and mixed metal parts and gears are crucial to enhance their performance, durability, and aesthetics. Here are some commonly used finishing techniques:
Electroplating: Applying a thin layer of metal onto the surface of the part using an electric current. This can improve corrosion resistance, reduce friction, and enhance appearance.
Anodizing: An electrochemical process that converts the metal surface into a durable, corrosion-resistant oxide layer. This is particularly common for aluminum parts.
Passivation: Treating metal with an acid solution to remove contaminants and enhance the formation of a protective oxide layer, especially useful for stainless steel parts.
Heat Treatment: Heating and cooling the metal to alter its physical and mechanical properties, such as hardness and strength.
Powder Coating: Applying a dry powder that is then cured under heat to form a protective and decorative layer. This provides a durable and high-quality finish.
Grinding: Using abrasive wheels to remove material and achieve a smooth surface with precise dimensions. This is commonly used for gears to ensure proper meshing and function.
Polishing and Buffing: Mechanical processes that use abrasives to create a smooth, reflective surface. Polishing removes minor imperfections, while buffing produces a high-gloss finish.
Shot Peening: Bombarding the surface with small spherical media to induce compressive stresses, improving fatigue resistance and reducing the risk of stress corrosion cracking.
Laser Cladding: Using a laser to melt and fuse a coating material onto the surface of the part, providing enhanced wear and corrosion resistance.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD): Depositing thin films of material onto the surface through chemical processes, providing excellent hardness and corrosion resistance.
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD): Depositing thin films of material through physical processes, such as sputtering, to achieve superior hardness and wear resistance.
Electropolishing: An electrochemical process that removes a thin layer of material to achieve a smooth, shiny finish and improve corrosion resistance.
Vibratory Finishing: Placing parts in a vibrating container with abrasive media to deburr, clean, and polish the surfaces.
Why Finishing Mixed and Rare Metals Requires Specialized Techniques
Finishing mixed and rare metals is particularly challenging due to their unique chemical and physical properties. These metals often have high strength, hardness, and corrosion resistance, which can make them difficult to machine and finish using standard techniques. The diverse compositions of mixed metals (alloys) can lead to varying reactions during finishing processes, requiring precise control and specialized knowledge to achieve the desired outcomes.
Rare metals, such as titanium and zirconium, have high melting points and react differently to heat and chemical treatments compared to more common metals. Additionally, their surface characteristics can be highly sensitive, necessitating careful handling to avoid damage or degradation.
Specialized Metal Finishing Machines
At James Engineering, we specialize in finishing a variety of mixed and rare metal parts using advanced multi-axis Surface Finishing machinery. Our equipment employs abrasive wheels, rotating brushes, and oscillating discs, enabling us to grind, deburr, round, and polish metal components in a single pass.
Manufacturing metal parts demands not only a deep understanding of materials and machinery but also a precise grasp of their intended applications. At James Engineering, we utilize state-of-the-art finishing machines to optimize the properties of mixed and rare metal parts for a wide range of industries. Our advanced deburr techniques ensure minimal material waste and deliver peak performance, making us a trusted partner for leading manufacturers worldwide.
Contact us today to learn more about our specialized metal part processing services and discover how we can enhance your manufacturing processes.
High Volume Metal Finishing with James Engineering’s MAX Systems
high volume metal finishing comes into play. Whether you’re producing aerospace gears, medical implants, or large industrial components, the ability to finish thousands of parts with uniform quality can make or break your production line.
In today’s fast-paced manufacturing world, precision and consistency aren’t just important—they’re essential for scaling production. That’s where high volume metal finishing comes into play. Whether you’re producing aerospace gears, medical implants, or large industrial components, the ability to finish thousands of parts with uniform quality can make or break your production line.
James Engineering has developed the most advanced high volume metal finishing machines available, engineered to deliver flawless results at unmatched speeds. From deburring and polishing to radiusing and chamfering, our MAX Systems streamline finishing for large-scale runs without sacrificing precision. For manufacturers looking to expand throughput while maintaining consistency, James Engineering is the partner you can trust.
Why High Volume Metal Finishing Matters
Metal finishing is more than just the last step in production—it’s a vital process that determines durability, safety, and appearance. For companies managing large-scale orders, traditional finishing methods often can’t keep up. Hand finishing, tumbling, or outdated systems may work for small batches, but they fall short when thousands of parts need to meet exact tolerances.
That’s where James Engineering comes in. As a high volume metal finishing company, we specialize in creating machines that are purpose-built for efficiency, reliability, and flexibility. With MAX Systems, manufacturers no longer have to choose between speed and accuracy—they get both in one optimized solution.
The MAX Advantage
Our flagship high volume metal finishing machine is designed with scalability in mind. Here’s what sets it apart:
Multi-Function Tooling – One system can polish, deburr, chamfer, and radius parts, minimizing downtime and eliminating the need for multiple machines.
360° Coverage – Every contour, edge, and surface is finished with precision, no matter how complex the part geometry.
Automated Workflows – Our machines can run fully hands off or have saved cycle “recipes” allowing repeatable runs with one touch, ensuring identical results across batches.
Scalable Throughput – From hundreds of parts to tens of thousands, MAX adapts seamlessly to your production demand.
By combining efficiency with precision, MAX Systems redefine what’s possible in High Volume Metal Finishing operations.
Consistency Across Industries
One of the greatest challenges in high-volume finishing is ensuring consistent results, even when switching between different materials or part designs. James Engineering machines are built to handle everything from lightweight aluminum components to hardened steel gears without sacrificing edge quality or surface smoothness.
This versatility is why our MAX Systems are trusted by OEMs across aerospace, automotive, defense, and industrial manufacturing. We’ve provided a step up on production for a wide variety of industries right in our hometown in Colorado and across coastlines, delivering solutions that scale globally.
A Smarter Investment in Manufacturing
Choosing the right high volume metal finishing machine isn’t just about solving today’s problems—it’s about preparing for tomorrow’s challenges. By investing in James Engineering’s MAX Systems, manufacturers gain:
Reduced labor dependency through full or semi-automated operation
Faster cycle times without downtime delays
Lower consumable costs thanks to longer tool life and compliant technology
Improved sustainability with optional wet cycles and fluid recycling
It’s not just a machine; it’s a long-term performance advantage for your shop floor.
Partner with James Engineering
At James Engineering, we don’t just build machines—we build partnerships. As a leading high volume metal finishing company, we work closely with manufacturers to design solutions tailored to their unique production goals. Every MAX System is customizable, ensuring you get a machine that not only fits your workflow but enhances it.
If your production demands are growing and your current systems can’t keep up or you’re ready for the next step, now is the time to upgrade. Contact James Engineering today to learn how our MAX Systems can transform your high-volume finishing operations and give your business the competitive edge it deserves.
Metal Buffing Machines Reimagined: How James Engineering Delivers Next-Level Finishing
Metal buffing machine technology has long been seen as a necessary but unremarkable step in the finishing process—until now. At James Engineering, we’ve redefined what a truly optimized industrial metal buffing machine looks like, from small to large, and made polishing smarter, faster, and more precise than ever before.
Metal buffing machine technology has long been seen as a necessary but unremarkable step in the finishing process—until now. At James Engineering, we’ve redefined what a truly optimized industrial metal buffing machine looks like, from small to large, and made polishing smarter, faster, and more precise than ever before. Whether you're looking for a standalone solution or an integrated system, our machines are built to meet every demand in modern manufacturing.
If you’re searching for a metal buffing tool that can handle complex parts, delicate edges, and tight tolerances, or simply exploring a more capable metal polishing machine, the MAX Systems by James Engineering sets the new benchmark. From small custom shops to high-volume OEM production, we offer more than just a metal buffing machine for sale—we offer a long-term performance upgrade.
Why Buffing and Polishing Matter More Than Ever
In today’s high-precision manufacturing environment, finishing isn’t just about aesthetics—it’s about functionality, durability, and reducing failure points. A properly buffed and polished component resists corrosion better, reduces friction, and performs more reliably over time. This is especially critical in industries like aerospace, defense, automotive, and energy where one flaw can cost millions.
Traditional machines often force manufacturers to choose between speed and precision. But James Engineering’s MAX Systems are designed to eliminate that tradeoff entirely. Our industrial metal buffing and polishing machines are capable of delivering consistent surface finishes at high throughput—without sacrificing control or customizability.
Aircraft part buffed by one of our MAX Systems machine
Multi-Function Flexibility Built Into Every MAX Systems Machine
The MAX Systems is not a single-purpose tool—it’s a modular platform engineered to handle buffing, polishing, chamfering, radiusing, and deburring in one streamlined cycle. Our machines come standard with quick-change toolheads, allowing users to swap between a metal buffer machine and a metal polishing machine setup in seconds. This versatility reduces downtime and allows one machine to perform the work of several, saving space and capital.
Whether you’re polishing micro parts with tight geometry or finishing large industrial components, MAX Systems scale accordingly. That means no more investing in both a small metal buffing machine and a large-format unit—James Engineering builds one system that can handle both ends of the spectrum with ease.
Precision That’s Built, Not Programmed
Other manufacturers may rely on rigid automation or basic tooling, but James Engineering incorporates a patented compliant technology that adjusts in real time to part geometry, pressure sensitivity, and tool wear. This ensures even material removal, longer tool life, and a buffed or polished finish that’s consistent across batches—no matter how complex or delicate the part.
Even when dealing with unpredictable part variables or inconsistencies, our system adapts automatically. Unlike conventional machines, MAX Systems doesn’t rely on operator intuition or trial-and-error cycles. Instead, it delivers precision with repeatable accuracy, every single time.
Lights-Out Buffing: True Automation Starts Here
James Engineering also leads the industry in fully automated, unattended operation. Our machines are built for 24/7 lights-out manufacturing, complete with programmable “recipe” cycles that can be saved, recalled, and launched with a single touch. That means your shop can run multiple parts or repeat single runs without setup delays—just load, press start, and walk away.
This is especially beneficial for manufacturers looking to reduce labor dependency, increase throughput, and eliminate costly human errors from the finishing process. Whether you’re processing a single prototype or running a multi-thousand-part batch, MAX Systems operate with maximum uptime and minimal supervision.
Built In-House, Built to Last
As a full OEM, James Engineering doesn’t source components from third parties—we engineer every feature of the MAX Systems ourselves. That includes the frame, control systems, tool heads, and even our own proprietary abrasive wheels, which are made with a liquid resin that promotes even wear and extended lifespan.
This in-house approach means our machines aren’t just customized—they’re optimized. Every MAX Systems machine can be tailored to your specific operation, material type, or finish requirement, and easily modified in the future as your production evolves.
Sustainable and Smart by Design
Sustainability in manufacturing is no longer optional—it’s essential. James Engineering’s MAX Systems machines support optional “wet” buffing and polishing cycles with an internal 150-gallon closed-loop filtration tank. This allows water and polishing fluids to be cleaned, recycled, and reused without waste or contamination.
Combined with our long-life abrasives and compliant technology that prevents over-grinding, MAX Systems extend tool and media life while reducing consumable costs. It’s a better finish with a smaller environmental footprint.
Ready to Upgrade? Here’s Why You Should
James Engineering offers more than a metal buffing machine for sale—we offer a comprehensive finishing solution that grows with your business. Whether you’re polishing turbine blades, medical implants, or large structural components, MAX Systems delivers a performance edge that’s hard to beat.
Stop wasting time on slow, single-purpose machines that limit your output. Upgrade to a system that’s engineered for precision, built for speed, and designed to last.
Talk to Us Today
If you’re ready to elevate your surface finishing operations with a truly advanced industrial metal buffing machine, get in touch with the team at James Engineering. We’ll help you configure a machine that fits your needs—whether you’re after a small metal buffing machine for specialized parts or a high-throughput system for full production lines.
Contact us today to schedule a demo, request a quote, or see the MAX Systems in action. (Click Here)
Metal 3D Printing Surface Finish | Solving Challenges with James Engineering
Metal 3D printing surface finish is one of the most critical challenges in additive manufacturing. While metal additive parts offer complex geometries and fast production, they often suffer from poor surface quality, rough textures, and inconsistent tolerances. That’s where James Engineering comes in—with purpose-built 3D printing finishing machines, intelligent 3D printing finishing tools, and precision-engineered 3D printing smoothing machines designed to elevate post-processing for additive parts.
Whether you’re producing lightweight aerospace brackets or medical implants with intricate contours, your additive manufacturing surface finish can’t be left to manual processes or inconsistent solutions. James Engineering’s MAX Systems offer an automated, reliable, and scalable way to achieve high-quality finishes that match or exceed traditional subtractive methods.
The Finishing Problem in Additive Manufacturing
Even with advancements in powder-bed fusion, DMLS, and other additive technologies, 3D-printed metal parts typically emerge with high surface roughness, partially sintered particles, and sharp micro-edges. These defects can compromise part performance, wear resistance, and even regulatory compliance.
Traditional surface finishing methods like hand sanding or tumbling are not only labor-intensive but also lack consistency—especially across batches or complex geometries. What additive manufacturers need is a system that can smooth, polish, and deburr with speed, accuracy, and repeatability.
MAX Systems: Purpose-Built for Additive Surface Finishing
James Engineering has developed a range of tools specifically designed to address additive surface finish needs. Our MAX System is a fully automated finishing platform that can be outfitted with custom heads for polishing, chamfering, deburring, and smoothing—all in a single cycle.
Thanks to our patented compliant technology, the MAX System can adapt in real time to the shape and material hardness of any 3D-printed part. This makes it ideal for finishing both high-value prototypes and production-grade parts with complex geometries and tight tolerances.
You no longer have to rely on inconsistent manual finishing or underpowered aftermarket solutions. Our 3D printing smoothing machines and tools deliver precision-polished results with minimal operator input and no part distortion.
From Micro Parts to Large Builds—No Size Limitations
Unlike traditional post-processing systems, James Engineering’s machines aren’t restricted by part size. Whether you’re processing small dental components or large-format structural parts, our MAX platform can scale accordingly. For shops running diverse builds from their printers, this is a game-changer.
Even better, our saved “recipe” functionality allows you to program and repeat finishing cycles with one button press. That means consistent finishing from the first part to the thousandth.
Built for the Future of Additive Manufacturing
With the rapid adoption of metal 3D printing in aerospace, defense, and medical industries, the demand for better finishing solutions has never been higher. Our systems not only meet that demand—they’re built to exceed it.
If you’re ready to take your metal 3D printing surface finish to the next level, contact James Engineering today. Discover how our purpose-built 3D printing finishing machines and tools can bring automation, consistency, and perfection to your additive workflows.
Surface Finishing Reinvented | Reshaping the Future of Metal Surface Finishing Machines
Metal surface finishing process demands precision, speed, and consistency—qualities that are essential in today’s competitive manufacturing landscape. From aerospace components to heavy machinery, every metal part must be properly treated to meet high-performance and durability standards.
The metal surface finishing process demands precision, speed, and consistency—qualities that are essential in today’s competitive manufacturing landscape. From aerospace components to heavy machinery, every metal part must be properly treated to meet high-performance and durability standards. That’s where James Engineering steps in. Our innovative metal surface finishing machines are redefining what’s possible in surface treatment by combining automation, flexibility, and unmatched precision.
Whether you're researching the types of metal surface finishing treatments, evaluating your current processes, or searching for the right “metal surface finishing machine near me”, James Engineering’s MAX Systems provide the industry’s most advanced and adaptable solution. We’re not just improving the types of surface finishing processes available—we’re building machines that evolve with your production demands.
What Is Surface Finishing of Metal?
Surface finishing of metal refers to processes that alter the surface of a metallic part to achieve a desired texture, smoothness, or protective layer. These treatments may serve aesthetic, functional, or performance-related purposes—ranging from removing imperfections to preparing a surface for coating or painting. The types of metal finishing vary widely, including deburring, polishing, chamfering, and radiusing.
Each of these methods serves a unique role in the production lifecycle, and finding the right metal surface finishing machine tools can be the difference between efficient output and costly downtime.
Introducing the MAX Systems: The Pinnacle of Surface Finishing Innovation
The MAX System from James Engineering is not just another machine on the floor—it’s the ultimate platform for all your metal surface finishing machine techniques. It’s engineered from the ground up to do more than just remove burrs; it delivers a complete finishing solution in one automated system.
Multi-Function Tooling for Any Finish
Unlike traditional equipment, MAX Systems allow for quick swapping of an unlimited array of tools. These tools can not only deburr but also chamfer, polish, and radius metal parts in one fluid cycle. That means fewer machines, faster cycles, and better results—all with a single investment.
With MAX Systems, your team can transition between types of metal surface finishing treatments with just a push of a button. It’s a true all-in-one solution, built to serve shops handling everything from high-mix low-volume parts to heavy-duty industrial runs.
The MAX Surface Finishing Cycle: Precision in Every Pass
At the heart of every MAX Systems machine is our custom-crafted surface finishing cycle, engineered for total precision and consistency.
360° COVERAGE
Our finishing process features complete 360-degree contact, reaching every contour and edge. This ensures that burrs, oxidation, or imperfections are removed uniformly, no matter the geometry or orientation of the part.
DYNAMIC ROTARY TABLE
The MAX Systems’ dynamic rotary table operates between 5 and 1000 RPM, rotating in both directions to tackle imperfections from every angle. This dual-motion design enhances precision while reducing cycle times. It's built to ensure that no spot goes untreated.
OVERHEAD SERVO & SMART TOOL SYSTEM
Using an overhead servo arm and high-durability tool options, the MAX Systems delivers delicate yet powerful finishing action. The tools adjusts in real-time to match part geometry, ensuring no over-grinding or missed zones. Whether you're preparing aerospace gears or large-scale industrial plates, the MAX Systems adapts to your needs with intelligent motion and force control.
DESIGNED FOR SPEED AND SIMPLICITY
Time is money in manufacturing, and the MAX Systems delivers where it counts.
LIGHTNING-FAST SETUP
Operators can load parts and initiate cycles with minimal effort. No complex retooling, no in-depth programming. Whether it’s your first shift or your 500th run, the MAX System’s interface and modular setup keep workflows efficient.
MINIMAL TRAINING REQUIRED
Built for intuitive use, the MAX requires little to no specialized training. This lowers barriers to entry, reduces errors, and ensures your team stays productive from day one.
CONSISTENT RESULTS ACROSS EVERY MATERIAL
MAX Systems are not limited by part size or material type. Whether you're working with stainless steel, aluminum, titanium, or exotic alloys, the MAX System delivers consistent, repeatable finishes. Our systems are built to handle both soft and hard metals without compromising on edge quality or surface smoothness. Even complex geometries or irregular contours are processed with precision thanks to adaptive tooling and intelligent motion control. This ensures every part meets strict quality standards—no matter the material or application.
Why James Engineering?
James Engineering has spent decades perfecting the art of metal surface finishing machine design. We’re more than a machine builder—we're a full OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) that controls every aspect of development, from hardware to software. This lets us optimize every feature for performance, reliability, and customer adaptability.
We don’t build “one-size-fits-all” machines. We build tools tailored for manufacturers who need flexibility, speed, and quality without compromise.
So whether you're rethinking your metal surface finishing process, upgrading outdated technology, or simply searching “metal surface finishing machine near me,” James Engineering is ready to help you finish stronger.
Experience the Future of Surface Finishing
From a wide range of types of metal surface finishing treatments to fully automated production lines, James Engineering is redefining what’s possible in modern manufacturing. Whether you're upgrading outdated equipment or expanding capacity, our MAX Systems are engineered to evolve with your production needs.
Trusted by top industry leaders, MAX Systems delivers intelligent automation, unmatched flexibility, and flawless results. With the ability to deburr, chamfer, polish, and radius—all in one cycle—our systems outperform traditional methods in both speed and consistency.
If you're searching for a metal surface finishing machine near me or exploring better metal surface finishing machine techniques, MAX Systems is the future-ready solution.
Don’t settle for the ordinary—invest in the extraordinary. Contact James Engineering today to learn how our MAX Systems can transform your finishing process and elevate your entire operation.
Robot Deburring Machines and Automated Deburring Tools
If you’re exploring options for a robot deburring tool, robotic deburring system, or automated deburring solutions you’re on the right path to upgrading your company. With the rise of automation, many manufacturers are evaluating robot deburring for sale to increase throughput and reduce manual labor. Although robot options with finishing tools have gained popularity, they often fall short in precision, adaptability, and long-term reliability.
If you’re exploring options for a robot deburring tool, robotic deburring system, or automated deburring solutions you’re on the right path to upgrading your company. With the rise of automation, many manufacturers are evaluating robot deburring for sale to increase throughput and reduce manual labor. Although robot options with finishing tools have gained popularity, they often fall short in precision, adaptability, and long-term reliability.
That’s why James Engineering has created the MAX Systems solutions to correct the issues posed by robotic deburring.
A Superior Alternative to Robotic Deburring
Unlike traditional robotic deburring systems, which rely on fixed-forced programming, rigid tool paths, or unreliable sensors, the MAX Systems is built with compliant technology that actively adapts to part inconsistencies. Beyond automation, our systems are intelligently optimized.
Where a robot deburring spindle might struggle with consistent part alignment, the MAX Systems mechanically adjust in real-time. This delivers a repeatable result without over-engaging the material or prematurely wearing out tools. This allows for better quality, longer tool life, and fewer scrap parts. To optimize our machines further, our MAX Systems can be operated with a push of a button or none at all with our fully lights out option.
Automated Deburring Done Right
While robotic systems tend to require extensive setup, programming, and calibration, the MAX Systems eliminates downtime between part runs. Especially if the next run part is completely different from the first. With built-in ‘recipe saving’ and push-of-a-button cycling, operators can switch from one part to another in seconds. And our fully automated machines run themselves with consistent and reliable results. That’s automated deburring at its best. We not only remove labor, but we also remove inefficiencies with our fully optimized machines.
In real-world production, a James Engineering machine has chamfer finished and deburred 82 different edges of a part in under 30 seconds, including any secondary burrs.
The real-time save though is what happens in between parts. Set-up times are eliminated, streamlining your production.
Multi-Function Capabilities Unlike Any Robot
When looking for a robot deburring machine or robot deburring cell, most solutions are limited to their functions, commonly requiring several operations for a single part.
Not our MAX Systems. It’s built from the ground up to be a multi-tool finishing platform, capable of supporting unlimited tool heads for a wide range of finishing operations. Deburring, chamfering, polishing, radiusing, and beyond. We’ve created the solution to expensive robot deburring kits that become an inflexible system. It’s all integrated and scalable with the MAX Systems.
Engineered for Precision and Repeatability
James Engineering’s patented compliant technology is what truly sets apart the MAX Systems. Unlike robotic arms, which are programmed for a fixed level of pressure and engagement, our compliant system compensates dynamically for wheel wear, part distortion, and inconsistent material flow. No matter the processing type, forged, stamped, or machined parts, the precision results are the same.
This is especially critical when working with micro parts or odd-shaped components. Robots tend to overwork or undercut edges due to their fixed program. James machines maintain consistent edge work even on the most complex geometries.
Built for Sustainability and Long-Term ROI
Sustainability is an issue with robotic deburring systems. High energy usage, expensive consumables, and inconsistent results that leap to scrap are to blame. We combat this with intelligent designs and superior materials.
From our own liquid resin grinding wheels to our recycled coolant system, we have optimized our machines for max sustainability. These thought-out features create longer tool life, even wear patterns, and reduce overall waste.
Plus, our patented technology reduces tool strain, meaning grinding wheels and deburring heads last far longer than traditional robotic setups.
Full OEM Control = Optimization Without Compromise
Another key differentiator is that we are a full OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer). The reason we have full optimization on every component of our machine is because they are all built in-house. This not only allows us to have full control of our machines, but also allows us to beat supply chain delays.
You won’t get that level of responsiveness from an off-the-shelf robot deburring tool or a third-party ati robotic deburring tool add-on.
Designed for the Future of Manufacturing
Robotic solutions may seem futuristic, but without real adaptability and control, they become a complicated way to automate yesterday’s problems. Robots are great for other areas of manufacturing, but when they are modified to do a job they weren’t originally designed for it gets complicated. James machines were designed from the start to be the best finishing machines on the market. Since their creation, they have been nothing short of the best, consistently providing for leaders of the industries.
With lights-out operations, intuitive controls, zero-setup part changes, and built-in sustainability features, James Engineering helps manufacturers do more without limitations.
Ready to Upgrade Your Manufacturing Process?
If you're evaluating your options among the robot deburring for sale, don't settle for a tool that limits your potential. Discover how the MAX Systems Machine from James Engineering can revolutionize your finishing process.
Contact us today to schedule a sample demo or talk to an expert. Watch the MAX Systems in action below and see why it’s the smarter, more capable alternative to robotic deburring.
Revolutionary Machining Tech | 'Skip Tooth' Finish
Our 'Skip Tooth' tech allows us to control what parts of a component we want to chamfer. Instead of running a whole edge, this operation can 'skip' over the part that doesn't need a chamfer…
Our 'Skip Tooth' tech allows us to control what parts of a component we want to chamfer. Instead of running a whole edge, this operation can 'skip' over the part that doesn't need a chamfer.
We can also program other motions and tools into this operation. Whatever your imagination can think of, we can do with our 11-axis MAX Systems machine.
Machine Finishing Made Simple | Push-of-a-Button Deburring and Chamfering
A Deburring machine for sale like no other. Our machines have helped streamline manufacturers' processes for 40 years. Big or small, the answer for how to deburr machined parts is here.
A Deburring machine for sale like no other. Our machines have helped streamline manufacturers' processes for 40 years. Big or small, the answer for how to deburr machined parts is here.
From deburring to chamfering, polishing to washing, and everything in between, our machines have got you covered. Whether you're dealing with gears or non-gears, micron-sized parts or massive components over 25 feet and 1000+ pounds, our systems are built tough to handle it all.
Choose from manual, semi-automatic, or fully automated options to suit your needs. Upgrading your finishing process has never been easier!
The Unique History of CNC Machining | Where Did Precision Machining Come From?
In this timeline we’ll look at when the first CNC machine was made, how it came to be, and a glimpse at the future of modern machining.
In this timeline video we’ll look at when the first CNC machine was made, how it came to be, and a glimpse at the future of modern machining.
(Computer Numerical Control)
Transcript:
What does Mickey Mouse and smoking have to do with the start of the CNC machines that make your phone and attribute to almost everything we use day to day? You’re about to find out.
Let’s jump back to the post World War II era. A cultural time when
Fears surrounding the Cold War would soon come to rise. Public hysteria surrounding ideas like the suspected "Bomber Gap," would increase the US military budget aiming to compete with Soviet production. This budget would motivate and lead to advancements in the machining world.
Starting in 1946, a time dominated by manual machining with the industry-standard “Bridgeport” mill, a man named John Parson would hire another man named Frank Stulen. They would work together on helicopters for Sikorsky Aircrafts.
Stulen started using simple calculations of 17 points to cut along for each component. This idea came from his brother working at IBM using a punch card reader.
(Punch cards are essentially the original lines of code. Operators would manually punch holes in cards representing machine instructions. The cards would then be fed to a machine. The card would read the card with sensors in order to perform its operation.)
There were inconsistencies in the cuts though. To solve that Parson suggested adding more coordinates to which Stulen created a 200 point program.
This would essentially create a labor intensive prototype for what now is a 2 1/2 Axis CNC machine.
This “by the numbers method” was still fully manual though. An operator would call out numbers off a chart while two other operators, on each the X and Y axis, would move the cutting head accordingly.
With the original inconsistencies out of the way, Parson envisioned the possibility of an automated machine with the use of Punch cards.
The problem? Funding. He was originally turned away by the Airforce, but in 1949 they came around and a 200,000 dollar contract was made, which equates to roughly 2.5 million in today's money.
Among others, MIT’s Servolab engineers would be brought on to the project. Unfortunately, the budget would run out. This would lead to a new bid for the government. MIT would underbid Parson essentially taking over the project and removing his company from further development.
The NC, Numerical Controlled machine would be finished and publicly displayed by 1952. MIT would finish their machine using a quicker 7 track punch tape instead of the original punch cards.
This was the same year a company named Arma Corporation who did defense work in the war would announce the first commercial numerically controlled lathe.
Throughout the rest of the 1950s Other NC machines were developed and improved upon. A report with Boeing noted “numerical control has proved it can reduce costs, reduce lead times, improve quality, reduce tooling and increase productivity” but even with glowing reviews the NC machine uptake was slow.
The US Army itself leased out 120 NC machines which finally began popularizing them.
Hand created Punch tapes still posed inefficiency to the machines. Time spent machining the parts was essentially substituted with time dedicated to creating the tapes. Author David Noble claimed this was the whole point as far as the Air Force was concerned; moving the process off of the highly unionized factory floor and into the non-unionized white collar design office.
The inefficiencies would change During the construction of MIT’s Whirlwind Navy Computer. John Runyon used the realtime computer to create these tapes by coding subroutines. Instead of producing a part in 8 hours, it could complete the job in 15 minutes.
Following this up was a proposal accepted by the Air Force to create a general programming language for Numerical Control in 1956.
This leads us to meet our next Duo of engineers, Doug Ross and Harry Pople. Along with a team, they would spend the next several years developing a language named, Automatic Programmed Tool, APT. In 1959 their developments would be presented to the press. The demonstration would feature their APT machined ashtray and a Mickey Mouse. Connecting the two social influences mentioned earlier.
APT and other programming languages would go on to revolutionize CNC machining.-
Though this is just the tip of the iceberg, these key moments would lay the foundation of today’s CNC machines. So where does James Engineering fall into all this? Even though our machines don’t use the now outdated punch cards or tapes, we do use punch cards to clock in and out.
But let's jump to early 1980s Formula One Racing. Our founder James “Jim” Richards, was working on Transmission solutions for the F1 cars. He was a key figure in Nelson Piquet winning several Formula One world championships starting in 1981 and Gordon Johncock winning the Indianapolis 500 in 1982.
He would see the need for precision chamfering and deburring in machining and eventually bring his pioneering advancements to the rest of the world. James Engineering’s machines would reach a broad spectrum of industries and top companies including Sirkorksy, Boeing, GE, and many more.
Though CNC machines have dominated the industry for a long period of time, the machining world is constantly evolving. Just as the whole industry, James Engineering is constantly making new advancements. With the rise of additive manufacturing, use of Artificial intelligence, and other technologies, one can only imagine what machining will look like 50 years from now.
What is Powdered Metal & What is the Process? | A look at Powder Metallurgy
In the evolving landscape of modern manufacturing, powdered metallurgy (PM) has emerged as a game-changer, offering a unique blend of precision, efficiency, and material innovation. But what makes this process stand out, and how are manufacturers overcoming its inherent challenges? Let's dive into the world of powdered metals, exploring their benefits, sensitivities, and the cutting-edge technologies transforming their finishing processes.
In the evolving landscape of modern manufacturing, powdered metallurgy (PM) has emerged as a game-changer, offering a unique blend of precision, efficiency, and material innovation. But what makes this process stand out, and how are manufacturers overcoming its inherent challenges? Let's dive into the world of powdered metals, exploring their benefits, sensitivities, and the cutting-edge technologies transforming their finishing processes.
What is Powdered Metallurgy?
Powdered metallurgy is a process where fine metal powders are compacted into desired shapes and then heated (sintered) at temperatures just below their melting points. This sintering process binds the particles together, creating cohesive and strong parts without fully liquefying the metal.
Why Choose Powdered Metals Despite Their Sensitivity?
1. Complex Geometries: PM allows for intricate shapes and internal features impossible with traditional machining or casting, like gears with complex tooth profiles or bearings with precise oil channels.
2. Material Efficiency: Up to 95% of the starting powder ends up in the final part, a stark contrast to machining processes where much material becomes scrap.
3. Material Innovation: Unique alloys, graded compositions, or metal-ceramic mixes are possible, enabling tailored properties for applications ranging from self-lubricating bearings to high-performance automotive parts.
4. Controlled Porosity: Engineered pores can hold lubricants or allow for controlled fluid flow, crucial in filters or heat exchangers.
5. High Production Rates: Once tooling is set, PM can rapidly produce consistent parts, ideal for high-volume needs like in the automotive sector.
6. Uniform Properties: The fine, uniform grain structure ensures consistent mechanical properties, enhancing fatigue and wear resistance.
What Makes Powdered Metal Parts Sensitive?
1. Green Strength: Before sintering, compacted parts (in their "green" state) are fragile and easily damaged.
2. Dimensional Precision: Many parts require tight tolerances; even slight variations can render them unusable.
3. Surface Integrity: Engineered porosity can be compromised by aggressive finishing.
4. Material Composition: Softer materials or lubricants in the mix can be damaged by abrasive techniques.
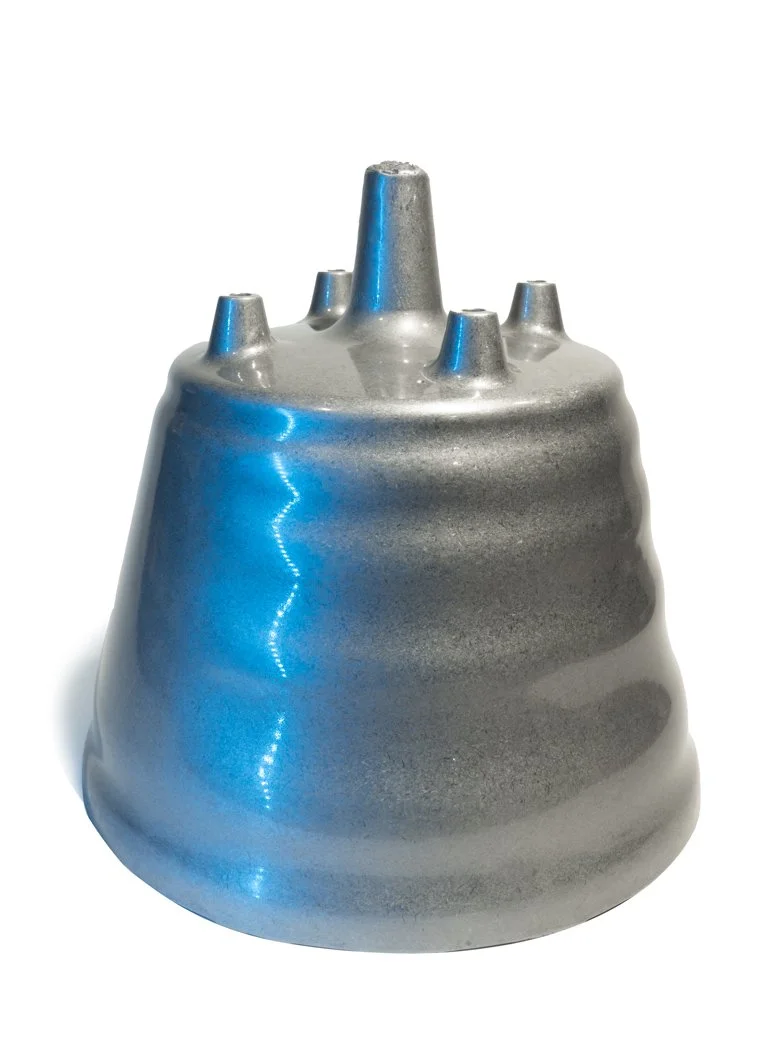
The MAX Deburring Machine, manufactured by James Engineering
Issues with Finishing | How Have Traditional Deburring Methods Fallen Short?
1. Manual Methods: Hand deburring risks human error and part damage.
2. Abrasive Tumbling: Often too aggressive, altering dimensions or over-removing material.
3. Nylon Disc Brushes: Gentler but requiring manual part flipping, introducing inefficiencies and potential errors.
Enter The MAX: A Revolution in Powdered Metal Finishing
James Engineering's The MAX exemplifies the evolution in PM part finishing:
1. Compliance Technology: It "feels" the part, adjusting pressure and action to ensure gentle, consistent deburring without damage.
2. Multi-functionality: Deburring, chamfering, radiusing, polishing, and washing in one machine minimizes handling of sensitive parts.
3. Automation: Eliminating manual flipping removes a key source of human error and boosts efficiency.
4. Precision Control: Fine-tuning of parameters allows optimized processes for varied part geometries and materials.
5. Consistent Quality: Every part receives the same gentle, precise treatment, batch after batch.
FAQ: What to Know About Powdered Metals
Q1: What industries use powdered metal parts?
A1: Automotive (gears, bearings), aerospace (turbine components), consumer electronics (motor parts), medical devices (implants), and more. Any industry needing complex, precise, or custom material properties can benefit.
Q2: How does powdered metallurgy compare to 3D printing (additive manufacturing)?
A2: Both offer design freedom and material efficiency. PM is typically faster and more cost-effective for high volumes, while 3D printing shines in low-volume, highly customized parts. Some processes now combine the two for optimal results.
Q3: Are powdered metal parts as strong as traditionally manufactured parts?
A3: Yes, and in some cases, stronger. The uniform microstructure and ability to incorporate strengthening elements can yield superior mechanical properties, especially in fatigue and wear resistance.
Q4: How does powdered metallurgy contribute to sustainability?
A4: By minimizing material waste (up to 95% utilization), reducing energy needs (no full melting required), and enabling lighter parts (important in transportation for fuel efficiency), PM is eco-friendly.
Q5: What's the future of powdered metallurgy?
A5: It's bright. Advances in powder production (finer, more uniform), sintering (faster, more controlled), and finishing (like compliance technology) are expanding PM's capabilities. Integration with AI for process optimization and the rise of metal 3D printing (a form of PM) are opening new frontiers.
Q6: How does the cost of powdered metal parts compare to traditional methods?
A6: Initially, tooling costs can be higher. But for medium to high volumes, PM often wins out due to faster production, less waste, reduced machining, and fewer assembly steps. The total cost of ownership is frequently lower.
Powdered Metallurgy for the future
Powdered metallurgy represents a confluence of precision, efficiency, and innovation in manufacturing. Its ability to create complex, high-performance parts with minimal waste makes it indispensable in our drive towards advanced, sustainable production. The sensitivity of PM parts, once a challenge, has spurred advancements like James Engineering's The MAX, ensuring that finishing processes match the precision of the PM process itself.
As industries worldwide seek ways to produce more with less, to innovate materials, and to automate for consistency, powdered metallurgy stands at the forefront. It's not just about making parts; it's about reimagining what's possible in materials and manufacturing. Whether it's the car you drive, the phone in your pocket, or the future of space exploration, the power of powder is quietly, precisely, shaping our world.
Machining's Most Difficult Chamfer | Automatic Part Finishing
This video shows a great execution of our precision. Our programming and compliant tech allow us to create targeted chamfers when the finish isn’t necessary for the whole part. We are also able to blend overlapping chamfers and avoid a rough transition. This is called a “Blended Chamfer”.
What is a Blended Chamfer?
This video shows a great execution of our precision. Our programming and compliant tech allow us to create targeted chamfers when the finish isn’t necessary for the whole part. We are also able to blend overlapping chamfers and avoid a rough transition. This is called a “Blended Chamfer”. Machinists and machines struggle with these precise finishes because there is so much room for error. If the chamfer is brought too far or not smoothly overlapped it risks a poor finish to the part.
Bump
The first motion of our operation for these gears is a ‘bump’. This seesaw motion can be performed very quickly and with our grinding wheels pressing all at once instead of dragging the edge it makes for an even quicker operation.
Interpolate
Following the ‘bump’ finish along the outer edge, our machine ‘interpolates’ the top of the gear. This is where the chamfer is blended into the first ‘bump’ finish creating a consistent edge. The customer’s gear shown here also had 3 different angles on the top of the teeth. Our machine matched each angle and performed the 3 different passes for each angle on the gear tooth.
Part Deburring Machine “Compliance” | The Missing Tech of Manufacturing
Part deburring machine manufacturers face several challenges with the tedious part finishing process. Whether it’s large or small parts, part deburring machines' biggest challenge may be an issue that isn’t discussed so often. That is machine compliance. Machine compliance is important not only in part machine finishing but also in almost every aspect of machining….
MANUFACTURING’S BIG PROBLEM
Part deburring machine manufacturers face several challenges with the tedious part finishing process. Whether it’s large or small parts, part deburring machines' biggest challenge may be an issue that isn’t discussed so often. That is machine compliance. Machine compliance is important not only in part machine finishing but also in almost every aspect of machining. Several methods have been developed to cope with this issue, but there’s one that proves to be a true solution to the problem. First, what exactly is machine compliance?
MACHINE COMPLIANCE
Though not as precise, we as humans can visually see and understand the dynamics of the part we are working on. We can make adjustments accordingly and make the needed changes for the differences part to part. When a robot or CNC is working on a part it is only comprehending the program it is running and not the actual part being machined. In a perfect world, every part would be the exact same and this would work great, but there is never a truly perfect part.
Even with smaller machined parts, unpredicted shrinking and expansion occur when cuts are made due to stress relief of the metal. This becomes a much more obvious problem with larger cuts or processes like forging, casting, or stamping that leave an excess flash seam. Burrs themselves also are never the same. These factors all impact the precision of the part and lead to unpredicted tool wear.
Abrasives used to deburr and finish parts tend to wear down at a quicker rate than normal tools. With even small inconsistencies the wear of the tools is hard to predict. This causes the machine to over or under-engage when machining a part.
OVER-ENGAGE
Over-engaging occurs when a machine gets too close to the part. Stress from the added force will cause tools to break and risk damage to the part itself. If a part is just slightly bigger than the original blueprint a machine running the same cycle will not make up for the difference in the part and will over-engage the part.
UNDER-ENGAGE
Under-engaging occurs when not enough pressure is applied or the tool misses the part completely. This will lead to poor precision or no finish at all on a part. Excess tool wear can be caused by the machine over-engaging and when a tool wears excessively the part will be under-engaged since there is less surface of the tool than expected.
Sensors and Algorithms
Sensors and algorithms have attempted to solve the issue of inconsistencies that lead to over/under-engaging but neither of these have proven to be a true solution. Because tool wear isn’t perfectly consistent, algorithms written to predict the wear result in varying levels of precision and fail over time. Sensors also pose more issues. With how abrasive finishing tools can be, excess abrasive and burrs can interfere with the sensor and lead to inconsistencies. Wet cycles that are run to keep down debris and clean the part cause the sensors to completely lose the surfaces and fail.
Mechanical Machine Compliance
The solution that has kept James Engineering’s part deburring machines running for 40+ years is our patented machine compliance. With precision axes and high-quality air motor tool arms, the tools can correctly comply with surfaces. Avoiding the use of sensors or algorithms, the part deburring machines take a mechanical approach to the issue. Once cycles are set up, the machine tools adjust part to part based on applied pressure.
Kitchen pot’s typical warping post machining. When spun on rotary table the difference of 1/8” can be seen. (James Engineering’s automated deburring systems)
Machine compliance is a critical but overlooked challenge in manufacturing and part machine deburring. Challenges lead to costly issues like tool wear, damage caused by over-engagement, and poor performance of parts due to the lack of precision. These problems not only increase operational costs but also require significant expertise to manage. Traditional solutions involving sensors and algorithms will fail due to the unpredictable nature of machining environments.
James Engineering's patented mechanical machine compliance eliminates these concerns. By automatically adjusting to each part’s unique characteristics without the need for sensors or algorithms, these part deburring machines eliminate the need for expert intervention, lower costs, and ensure consistent, high-quality finishes.
Automatic Polishing Machine Advantages
Automatic metal polishing and traditional polishing have always been a crucial part in the manufacturing process. Polishing provides essential finishes across many industries.
The Evolution of Automatic Metal Polishing
Automatic metal polishing and traditional polishing have always been a crucial part in the manufacturing process. Polishing provides essential finishes across many industries. Automatic polishing machines and automatic polishing tools have transformed the field. This article explores the differences in automatic polishing for metal, its advantages over manual polishing, and the significant impact of this technology on modern manufacturing, especially in the context of metallography and polishing for various types of metals from stainless steel to aluminum.
Basics of Metal Polishing
Metal polishing or buffing is the process of smoothing and shining metal surfaces. It is commonly achieved by rubbing or chemically treating the surface. The process of polishing can remove oxidation, and create a reflective surface, and is important for improving the appearance and functionality of the metal parts. Automotive, aerospace, the medical industry, and consumer electronics are just a few major industries that rely on polishing.
Manual vs. Automatic Metal Polishing
MANUAL POLISHING: THE TRADITIONAL APPROACH
Manual metal polishing is typically labor-intensive and heavily relies on a skillful and experienced operator. It involves handheld tools, abrasive materials, and various polishing compounds. While the manual approach can produce effective results, manual polishing has several disadvantages:
Inconsistency: Even with a skillful operator it is impossible to produce the same result every time so human error needs to be factored in. Varying results in finish quality can affect the uniformity of the final product.
Time-Consuming: Manual polishing is a slow process that can minimize production efficiency.
Safety Concerns: Manual polishing can create dangerous dust and hazardous materials posing health risks to workers.
AUTOMATIC POLISHING: THE MODERN SOLUTION
Automatic metal polishing machines address and solve the issues associated with manual polishing. These machines can use robotics, CNC (Computer Numerical Control) systems, or other technologies with specialized polishing tool heads. Key advantages include:
Consistency and Precision: Automatic machines can consistently produce high-quality finishes without inconsistencies.
Speed and Efficiency: Automatic polishing machines run much faster than manual methods and avoid the inefficiency of human fatigue.
Cost-Effective: By avoiding the risk of scrapped parts due to human error, automatic machines can cut financial costs in more ways than one. With a one-time purchase too there is no consistent cost with the machines.
Safety and Environmental Benefits: Enclosed polishing systems trap harmful dust and material creating a safer work environment.
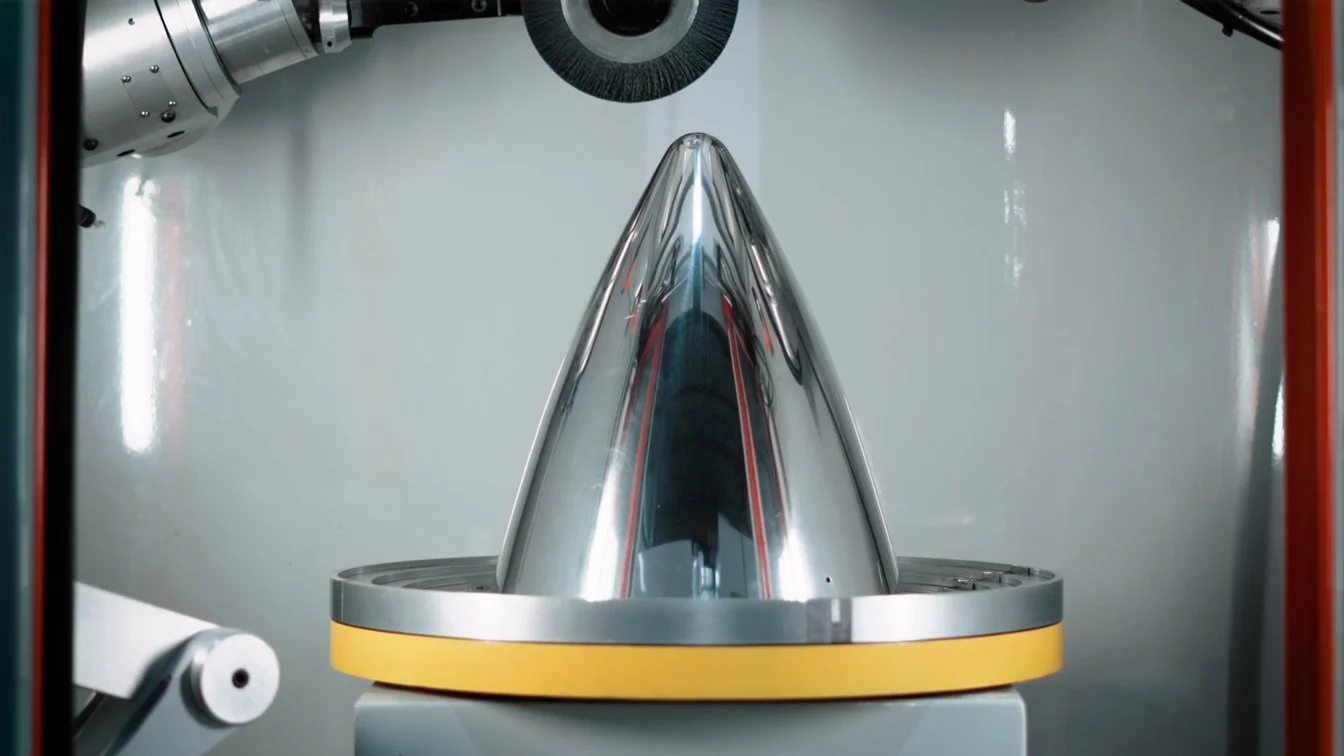
Airplane Engine Nosecone Polished by a James Machine
Case Study: Enhancing Automatic Polishing with the Max Systems Machine
James Engineering has developed an automatic polishing machine, a one-stop shop for surface finishing. The fully optimized MAX Systems Machine goes above and beyond a typical automatic deburring machine and solves issues that are still associated with automatic polishing.
Key features of the MAX Systems Machine:
Full Surface Finishing: Aside from polishing, James Engineering’s machines can be equipped for any other simultaneous surface finishing including, deburring, chamfering, radiusing, etc.
Unmatched Consistency: Typical automatic machines lack machine “compliance”. This means that tool wear and inconsistently shaped parts will create differences in polishes part to part. James Engineering’s patented technology mechanically makes up for this and can comply with any differences from part to part, producing a perfect finish every time.
User-Friendly: Our machines are designed to be run by any operator. With the simplest control panel, there is no worry about finding an expert operator. These seamless controls also contribute to the efficiency of the MAX Systems Machines.
Sustainable Wash System: The MAX Systems enclosed system not only isolates hazardous dust and materials but also can be equipped with a recycling wash system further adding to the sustainability of these machines.
Machine Memory: All James Engineering machines are equipped with “recipes” (saved part cycles). They can easily be called up allowing for change overtimes to only amount to a few seconds, even when swapping to a complex part.
The Future of Metal Polishing
Automatic metal polishing represents a significant advancement from traditional manual methods, offering numerous benefits in terms of consistency, efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and safety. As technology continues to evolve, the gap between manual and automatic polishing will only widen, solidifying the latter as the preferred choice for high-quality metal finishing.
For manufacturers seeking to enhance their production capabilities, investing in automatic polishing solutions like a MAX Sytems Machine can provide a competitive edge and drive long-term success.
The Untold Story Of American Independence: Machining America’s Freedom
Less recognized is the critical role that manufacturing and metal machining played in the contributions to sustaining America’s fight for freedom.
The American Revolution is commonly painted with scenes of brave soldiers fighting for liberty, defiant patriots signing the Declaration of Independence, or leaders such as George Washington and Thomas Jefferson.
What’s less recognized is the critical role that manufacturing and metal machining played in the contributions to sustaining America’s fight for freedom.
Industrial and technological advances were transforming the colonies in the 18th century. As economies diversified, the need for precision-crafted tools, weapons, and machinery became increasingly important. The efficient production of raw materials and manufactured goods for war gave a major advantage to the revolutionary forces.
Unsung Heroes
Blacksmiths were the unsung heroes of the American Revolution. They were the key in forging swords, muskets, pistols, canons, and other metal implements that armed colonial militia. They were also the producers of horseshoes, wagon parts, nails, and hardware needed to equip the revolutionary forces. During the Battle of Saratoga, a key turning point in the war, blacksmiths quickly repaired broken cannon carriages and other equipment giving them a huge advantage.
The Battle of Saratoga
Saugus Iron Works
Aside from blacksmith forges, the colonies had a machine tool industry that manufactured precision parts and munitions. Water-powered sawmills, mills, and grist mills processed raw materials like gunpowder and other raw materials. On top of being economic engines, these factories were important suppliers of military goods.
Saugus Iron Works
The most famous factory was the Saugus Iron Works in Massachusetts. It would produce pig iron, wrought iron, and a variety of other metal products. Saugus Iron Works would shift during the war into manufacturing cannons, musket barrels, and other armaments for the Continental Army. The shift from commercial to military production was one of the best early examples of America’s manufacturing capabilities.
This domestic production also allowed the Continental Army to avoid relying on foreign imports that would be subject to British naval blockades.
An American Long Rifle
Crafting Independence
From efficient and domestic manufacturing to quick repairs of firearms the progression of machine tools and manufacturing undoubtedly played a key role in the war’s outcome. Being products of the war, these advancements would set the stage for the Industrial Revolution and lay a foundation for the machining and manufacturing we have today.
In more ways than one, the American Revolution was won in the machine shops, forges, and mills of the colonies. The story of America’s founding is incomplete without recognizing the significant metal machining and manufacturing advancements.
Learn more about James Engineering’s contributions to American manufacturing!
Metal Deburring Machine & Other Removal/Surface Finishing Methods
Challenges in Traditional Burr Removal Methods:
Traditional deburring methods such as manual, mechanical, or even some automatic techniques pose challenges for optimal results. Inconsistent finishes, secondary burrs, or damage to the component that could lead to a scrapped part are all products of these traditional methods.
Manual Deburring: Manual deburring involves handheld tools such as a file, deburring knife, or abrasive pads. While this method offers control, it is labor-intensive, time-consuming, and impossible to produce consistent results. This also makes it less suitable for high-volume productions.
Mechanical: Mechanical deburring uses simple devices like automatic hand tools or tumblers. Though less labor-intensive than manual methods, each form carries its disadvantages. Automatic hand tools are still inconsistent while devices like tumblers or vibes could still slow down production with long cycle times. Errors of collusion could also result from batch processes and these devices will put a finish on the whole part when something more precise may be needed.
Automatic: Automatic deburring also comes in several forms. Machines like typical CNCs or robotic arms can be attached with tools for burr removal. Typical CNCs aren’t originally meant for the deburring process though. Specific abrasives used for deburring can damage these CNC machines when broken down, especially at the volume required for deburring. They also require complex programming that heavily relies on well-versed operators. One of the biggest issues with these CNCs and robots is being able to compensate for the differences between a physical component and its design. No part is exact, especially with processes such as forging or casting where flash is created. Tool wear is also something these machines can’t understand. They lack “Machine Compliance” and will lead to over/under-engaging causing broken tools or inconsistent parts.
MAX SYSTEMS Machine
“Machine Compliance” is a technology that James Engineering patented. MAX Systems mechanically make up for inconsistencies allowing them to repeatably produce perfect finishes. Cycle times are typically finished in seconds, but more importantly, the change over time can also be completed in seconds even for a completely different part. James’ machines have an extensive memory on them allowing for “recipes” to be called up for each part with just a push of a button. They also don’t require experienced operators, they are designed for anybody to run with a user-friendly control panel. Though these machines are designed for deburring and chamfering they have the capability to produce a diverse array of finishes.
The Need for an Optimized Metal Deburring Machine
Traditional deburring methods, including manual, mechanical, and even some automatic techniques, often fall short of delivering optimal results. Manual deburring is labor-intensive and inconsistent, making it unsuitable for high-volume production. Mechanical deburring methods, like automatic hand tools and tumblers, can be inefficient and prone to errors, while typical CNC machines and robotic arms face challenges with programming complexity and tool wear, leading to inconsistent outcomes.
By prioritizing advanced deburring and chamfering technologies, James Engineering ensures precision, consistency, and quality in metal part finishing, setting a new standard in the industry.
Valve Deburring Machine | Revolutionizing The Manufacturing Process
Whether it’s a valve deburring machine for hydraulics or any other industry, James Engineering’s MAX Systems machine has streamlined the finishing process for valves. The MAX Systems Deburring Machines possess the versatility to serve many industries and different types of deburring processes, but unique advantages heavily apply to valve part finishing. No matter how many valves your part has Max Systems machines will handle them in one operation with consistent precision.
A seamless process is essential for ensuring the smooth operation and longevity of valves as well as efficiency in the manufacturing process. Regarding accuracy, efficiency, and sustainability in valve deburring, the cutting-edge solutions provided by James Engineering are unmatched.
Introducing The MAX Systems’ Advanced Valve Deburring Machines
James Engineering has created a machine fully optimized for valve finishing. For example, several overhead servo arms are equipped with the ability to host an unlimited amount of different tools, whether it be a type of “abrasive” or a “flexible honing” tool.
Another reason a James’ Machine stands out is for the extensive memory it holds. Once you record an operation with as many stops as needed, the user-friendly control panel allows you to call up and repeat the process. Other machines will show inconsistency over time when running the same operation. This is caused by wheel wear or miss-shaped parts, but James’ patented technology of “machine compliance” overcomes this issue and prevents the need for any future adjustments or tweaks.
Efficiency at Its Core
Components with valves come in many shapes, sizes, and complexities. Many times these valves do not exist on a 2-dimensional plane and cause several different machine setups before a part is finished. The Max Systems Machines overcome this by having a full 360-degree range for each tool and a precision rotary table that can angle parts to MAXimize efficiency.
With several tools, MAX Systems are designed to perform multiple tasks simultaneously, significantly reducing cycle times and boosting productivity. Parts with complex valve geometries are finished in seconds, ensuring production lines keep moving without unnecessary delays.
A key feature of MAX efficiency is the automated setup and operation. Our machines require minimal setup time and can seamlessly transition between different parts. Operators of any skill level can easily manage the deburring process, ensuring consistent output without extensive training.
Unmatched Accuracy
Our machines utilize cutting-edge compliant technology that ensures consistent deburring results, regardless of part variations or tool wear. This technology allows for the precise removal of burrs without compromising the integrity of the valve components.
Additionally, our deburring machines are capable of handling intricate and complex valve designs. Whether dealing with micro-parts or oddly shaped components, our machines deliver perfect, repeatable, deburring, minimizing stress points and enhancing the overall quality of the valves.
Commitment to Sustainability
Sustainability is more than just a buzzword—it’s a necessity. James Engineering is dedicated to creating solutions that are not only efficient and precise but also environmentally responsible. The programmable cycles that can be saved as "recipes," on the MAX Systems Machines ensure consistent and repeatable results while minimizing waste.
Furthermore, Max Systems machines have optional “wet” cycles that utilize a filtered and recycled 150-gallon tank, maximizing water usage and reducing environmental impact. James Engineering also produces their own grinding wheels with a liquid resin that extends tool life, promoting even wear and reducing the frequency of replacements.
The Future of Valve Deburring
The innovative valve deburring machines from James Engineering show significant advancement in the manufacturing world. By integrating efficiency, precision, and accuracy into a single, cohesive solution, the Max Sytems are helping manufacturers elevate their production standards and achieve new heights of operational excellence.
Discover how our advanced deburring technologies can transform your operations and deliver superior results. Watch our machines in action and see the difference for yourself.
Smallest Gear in the World
The Smallest Gear in the World?
How small is the World’s smallest gear and how are these nano gears created, but more importantly what are they used for?
How small is the World’s smallest gear and how are these micro-gears created, but more importantly what are they used for?
How Are The Smallest Gears Made?
Let’s first understand how these microscopic-sized gears and robots are created. Researchers at Cornell and the University of Pennsylvania have created four-legged microscopic robots. They’re capable of moving when stimulated by light directed with a laser. Using a similar process to creating microchips, these researchers have created miniaturized devices that can be equipped with legs. The legs are built with a platinum sheet layered with an inactive material such as graphite. A pattern in the inactive material allows the legs to move when stimulated.
3D render of Cornell’s and the University of Pennsylvania’s microscopic robot
The University of Pennsylvania’s bacteria controlled gear
Another way these tiny components are created is by shining light through small photo masks onto a plastic compound. The compound will harden into the desired shape and is ready to be given functionality. Unlike the computerized approach to functionality, two researchers, also at the University of Pennsylvania, have used swarms of bacteria to control their microstructures. Control comes from the chosen shape of the gears and by manipulating the bacteria with blue light.
These tiny robots and structures are both microscopic, but let's consider two gears at the nano-scale that have been easily measured by a counting of atoms.
The World of Nanometers
It has been analogized that there are more atoms in a single grain of sand than there are grains of sand in the world. This means a single grain of sand possesses more than 100 quintillion atoms. Atoms exist on such a small scale, of 0.5 nanometers, that they cannot be observed with light microscopes. The wavelength of visible light is around 540 nanometers, making anything smaller than approximately 200 nanometers appear blurry.
To overcome this limitation, scientists use techniques that involve shorter wavelengths. For example, electron microscopes use electrons, which have much shorter wavelengths, to generate detailed images of nanoscale objects, such as tiny gears.
These advanced techniques allow us to see and manipulate structures at the nanoscale. So exactly how large are these nanoscale gears, and how have they been created?
Institute of Materials Research and Engineering Singapore’s Molecular Gear
Molecular Gear Wheels
If we took a trip to Germany to visit the University of Erlangen-Nuremberg we’d have to zoom in a lot closer to see the research being conducted on molecular gear wheels. Using a molecule called an “interlocked triptycene” and a fragment of a “thioindigo” molecule, the researchers created a gear controlled by light. This gear measured 1.6 nanometers and was made up of only 71 atoms.
So does this answer the question of the world’s smallest gear?
Before that can be answered we have to look at the Institutes of Materials Research and
A GUINNESS WORLD RECORD
Engineering Singapore which similarly constructed a molecular gear. This gear was created with one “pyrimidine core” and five “phenyl rings” all connected to a central “planar phenyl” molecule (hexa-t-butyl-pyrimidopentaphenylbenzene (C64N2H76; HB-NBP)). This molecular gear would measure 1.2 nanometers and consist of roughly 53 atoms. It was controlled using an electrical connection. This would lead Guinness World Records to officially recognize Singapore’s IMRE for creating the first working molecular-sized gears with full controllability.
So aside from all the technical science, what are these tiny gears and structures used for, or should we ask what will they be used for?
A Future of Solutions
While these studies have yet to fully be applied to direct applications in our everyday lives, they pave the way for a promising future where advancements in nanotechnology catch up with our imagination. Imagine a world where medicine can be precisely delivered to specific parts of the body, where cancer can be fought at the molecular level, and where individual cells or molecules can be manipulated for various purposes. Picture a future where nanotechnology aids in tasks from pest control to cleaning up oil spills or even collecting data. This future isn’t too far away either, for example, nanoengineers at the University of California San Diego have already successfully cleared bacteria of deadly pneumonia in the lungs of mice resulting in a 100% Survival rate. As we continue to push the boundaries of what is possible at the nanoscale and micro machines, we move closer to unlocking the practical applications that will shape our future.
Medical screw processed with our MAX Systems
Although there isn’t a need for a machined finish on these microstructures yet, we at James Engineering do deburr gears and components down to 1/16th of an inch. And who knows, with our constant advancements, you just might one day see an atom-sized chamfer from us.
To learn more about our contribution to advanced technologies and machining, reach out or contact us at James-Engineering.com